Paresthesias - what can frequent tingling of the extremities mean?

Paresthesias, or tingling commonly, is a seemingly trivial ailment, which is often neglected by many. Meanwhile, although it is not painful, it is very inconvenient for patients and, what is important, it can be a symptom of serious, chronic diseases, especially when it occurs often. What health problems can herald limb paresthesias and how to counteract them?
What is paraesthesia and how does it manifest itself?
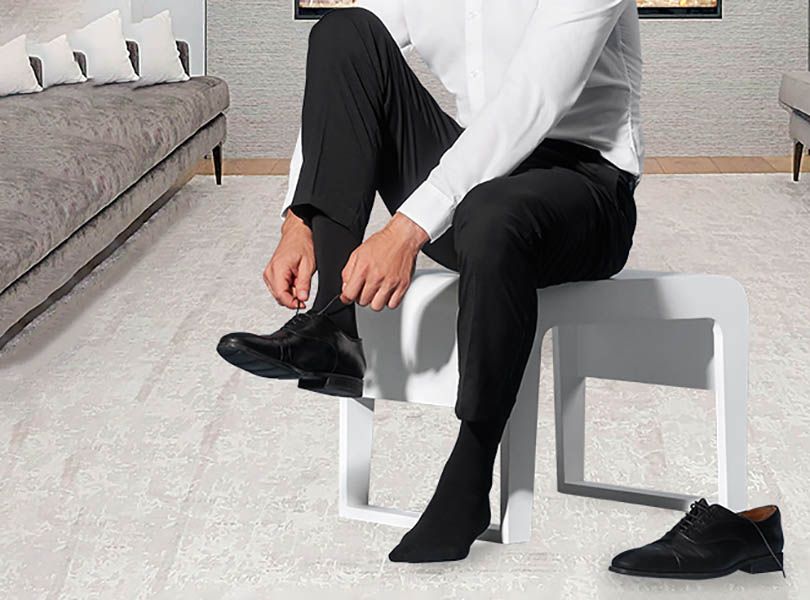
Paresthesia is the medical term for the so-called tingling sensation, often also felt as numbness in the limbs. This phenomenon may affect both the lower and upper limbs - in this form it occurs most often. However, paresthesias can actually affect any part of the body.
In medical language, this term is used to describe abnormal perception of external stimuli by the patient, which occurs as a result of disorders within the peripheral nervous system (polyneuropathy).
As a result, spontaneously occurring so-called sensory impressions can appear in the patient with varying frequency. These can take the form of the previously mentioned tingling and numbness, as well as pricking and burning sensations.
A symptom characteristic of paresthesia is the feeling of a distinct change in skin temperature - warm or cold - in the area of the damaged nerve.
Sometimes the patient may also experience additional symptoms, such as general weakness, temporary paralysis, visual and speech disturbances, and temporary loss of control of the upper or lower limbs, depending on the location of the paresthesia, manifesting for example as a lack of sensation in a finger, or even the whole hand or foot.
If you experience any of these symptoms, you should consult your doctor as soon as possible.
It is worth remembering that although occasional tingling in the fingers or numbness in the calves does not always have to be a cause for concern, and only a result of keeping the body in one position for a long time, often occurring paresthesias of the extremities may signal serious health problems.
They usually appear suddenly. It also happens that they disappear spontaneously just as quickly. Sometimes, however, the tingling in the calves may be experienced by the patient for a longer period of time or may recur frequently.
Causes of paresthesia
The causes of tingling in the extremities can be very diverse. Tingling in the leg can be both the result of deficiencies of certain vitamins, nutrients (e.g. calcium, potassium or vitamin B12), as well as the result and at the same time also a symptom of serious diseases and conditions within the whole body.
The most frequently occurring ones include:
- discopathy,
- degenerative changes of the spine,
- diabetes (especially if incorrectly treated),
- damage to the peripheral nervous system, affecting individual nerves,
- damage to the central nervous system,
- multiple sclerosis,
- thyroid disorders - hypothyroidism,
- atherosclerosis,
- carpal tunnel syndrome,
- kidney stones,
- neoplastic diseases,
- herpes infection (both active form and past treatment),
- psychosomatic disorders, including neuroses (especially anxiety neuroses),
- cerebral hypoxia,
- stroke,
- migraine headaches,
- poisoning by toxins,
- use of certain drugs,
- alcohol abuse.
Numbness of the calves may also occur in pregnant women. In this case, however, it is temporary. On the other hand, the degree of severity of paresthesia may vary - from weak, almost imperceptible tingling, up to distinct and strongly troublesome numbness of the extremities.
How to recognize the causes of tingling sensations in the extremities?
Numbness in the thigh, knee, hand or fingers does not always indicate a serious health problem. Sometimes the tingling sensation, which appears sporadically and disappears quickly, is simply the result of long-term compression of one of the nerves in the limb.
This phenomenon may occur, for example, as a result of keeping the body in one position for a long time or deficiencies in certain nutrients. However, if the tingling of the limbs occurs quite often, then it requires medical consultation.
Due to the fact that paresthesias can be a symptom of many diseases and conditions, determining their unambiguous cause often requires extended diagnostics. This is usually based on a detailed clinical history combined with a physical examination.
In addition, the doctor may order electromyography (EMG) and electronegraphy (ENG) tests.
The results of both provide basic information about the nature of the paresthesia including the severity, type and extent of the changes. In this way they can determine the type of nerve damage that has occurred in the patient.
Occasionally, cerebrospinal fluid examination may also be necessary. Ultrasound and X-ray examinations may also be helpful.
Paresthesias - treatment
Treatment of paresthesias primarily involves removing the main cause responsible for the occurrence of tingling sensations in the extremities.
Depending on its nature, it may therefore involve, among other things, balancing blood sugar levels, correcting nutritional deficiencies and restoring normal thyroid function.
Sometimes, in the case of strong sensory sensations felt by the patient, local symptomatic treatment is applied, recommending various types of anaesthetic creams.
In the case of recurrent paresthesias, prevention also plays a very important role, largely based on a healthy, balanced diet that provides all the necessary nutrients.